A Fighter by Aircraft Manufacturing Company.
Engine: 1 Gnome Monosoupape-rotary engine of 75 kW (100hp) (and later a 82 kW Rhône rotary)
Armament: 1 7.62 mm Lewis machinegun with 47-rounds discs)
Forming the equipment of the first British single-seat fighter squadron, the D.H.2 was introduced in 1916 as a sturdy biplane to counter the Fokker E-series. A pusher configuration was selected as the UK lacked a gun interrupter gear; the original mounting allowed elevation of the gun, but this was soon turned into a fixed mounting as pilots learned to aim the complete aeroplane at the target, using the highly responsive controls to wring the best performance out of this nimble machine. Production amounted to some 400 aircraft, and from spring 1916 the D.H.2 was instrumental in defeating the ‘Fokker Scourge’ and thereby giving the British air superiority. For lack of a replacement the type soldiered on into mid-1917. (Source: The International Encyclopedia of Aircraft, Oriole Publishing, 1991)
Span: 8.61 m (28.2 ft)
Length: 7.68 m (25 ft)
Height: 2.91 m (9.5 ft)
Wing surface: 23.13 m² (248.97 ft²)
Empty weight: 428 kg (943 lbs)
Max. Weight: 654 kg (1442 lbs)
Max. speed: 150 km/h (93 mph)
Ceiling: 4265 m (13.993 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Bomber by Aircraft Manufacturing Company.
Engine: 1 water-cooled 12 -cylindre Rolls-Royce Eagle VIII 280 kW (375 hp)
Armament: 2 7.7 mm Vickers machine-guns + 2 7.7 mm Lewis machine-guns + 209 kg bombs
The D.H.4, one of the most successful aircraft of the First World War, was specially developed as a bomber. After its maiden flight in August 1916, it was fitted with a Rolls-Royce Eagle engine, which improved its flight performance. Approximately 6,300 units were built, more than two-thirds of which were in the United States. Production continued even after the end of the war, and D.H.4s entered service with various air forces and some of the first airlines. (source: Aircraft of the World, IMP BV)
Span: 12.92 m (42.3 feet)
Length: 9.35 m (30.6 ft)
Height: 3.35 m (11 ft)
Wing surface: 40.32 m² (434 ft²)
Empty weight: 1083 kg (2387 lbs)
Max. Weight: 1575 kg (3472 lbs)
Max. speed: 230 km/u (143 mph)
Ceiling: 6705 m (21.998 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Fighter by Aircraft Manufacturing Company.
Engine: 1 Le Rhône 9 82 kW (110 hp)
Armament: 1 x 7.7 mm machine gun + 4 x 11.3 kg bombs
The D.H.2 had offered its pilot an excellent field of vision, and in designing the D.H.5 as its replacement with a tractor engine and interrupted gun, de Havilland chose backward stagger of the wings to give the pilot equally good fields of vision. In other respects the D.H.5 was thoroughly conventional, with a wire-braced wooden structure, fabric covering and fixed tailskid landing gear. The first example flew late in 1916, and despite performance considerably lower than that of the contemporary Pup an order was placed for 400 aircraft, of which the first began to enter service in May 1917. Only five squadrons received the type, whose indifferent air-combat capability led to rapid relegation to the ground-attack role. Here the D.H. proved far more suitable, and orders for another 150 were placed, though not all had been built before the type was withdrawn at the end of 1917. (Source: The International Encyclopedia of Aircraft, Oriole Publishing, 1991)
Span: 7.82 m (25 ft 8in)
Length: 6.71 m (22 ft)
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight: 667 kg (1492 lbs)
Max. speed: 165 km/u (102 mph)
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
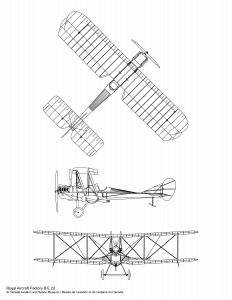
A General aircraft by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine:
Armament:
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed:
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Reconnaissance aircraft and light bomber by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine: Air-cooled 8 cylinder RAF 1a inline engine 67 kW (90 hp)
Armament: 1 7.7 mm MG and 100 kg bombs
Span: 11.3 m (37 ft)
Length: 8.3 m (27.2 ft)
Height: 3.4 m (11.1 ft)
Wing surface: 34.47 m² (371 ft²)
Empty weight: 621 kg (1369 lbs)
Max. Weight: 1077 kg (2374.3 lbs)
Max. speed: 138 km/h (85.7 mph)
Ceiling: 3050 m (10.000 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate: 1066 m (3497 ft) in 10 minutes
A Reconnaissance aircraft and light bomber by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine:
Armament:
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed:
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Reconnaissance aircraft and light bomber by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine:
Armament:
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed:
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Reconnaissance aircraft and light bomber by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine:
Armament:
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed:
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
B.E.2g
A Reconnaissance aircraft and light bomber by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine:
Armament:
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed:
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Dual Fighter by Bristol Airplane Company.
Engine:
Armament:
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed:
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Fighter by Bristol Airplane Company.
Engine: 1 x 12-cylindre Rolls-Royce Falcon III line-engine 205 kW (275 p)
Armament: 3 x 7.7 mm machine-guns + 108 kg bombs
In the period after the First World War, when the Royal Air Force was reducing its fleet, the Bristol F.2B Fighter was one of the most important British fighter aircraft for many years. After RAF pilots had suffered heavy losses during the war with the older F.2A, new, more successful mission procedures were developed for the F.2B. As a liaison and light attack aircraft, it remained in service with the armed forces until the 1930s. (Source: Aircraft of the World, IMP BV)
Span: 11.96 m (39 ft)
Length: 7.87 m (25.8 ft)
Height: 2.97 m (9.7 ft)
Wing surface: 37.62 m² (405 ft²)
Empty weight: 975 kg (2149 lbs)
Max. Weight: 1474 kg (3249 lbs)
Max. speed: 198 km/h (125 mph)
Ceiling: 5485 m (17.995 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate: to 3048 m (10.000 ft) in 11'15"
A Fighter by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine: Liquid-cooled Beardmore inline 119.3 kW (160 hp)
Armament: 1 or 2 7.7 mm Lewis machine guns and an external bomb load of 235 kg)
Span: 14.55 m (47.47 ft)
Length: 9.83 m (32.2 ft)
Height: 3.85 m (12.6 ft)
Wing surface: 45.89 m² (494 ft²)
Empty weight: 935 kg (2061 lbs)
Max. Weight: 1378 kg (3038 lbs)
Max. speed: 147 km/h (91 mph)
Ceiling: 3353 m (11.000 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine:
Armament:
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed:
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Fighter by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine: 1 Gnome Monosoupape-rotary engine of 75 kW (100hp) (and later a 82 kW Rhône rotary)
Armament: 1 7.7 mm machinegun
Span: 9.6 m (31.4 ft)
Length: 7.21 m (23.6 ft)
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight: 610kg (1345 lbs)
Max. speed: 152 km/h (94 mph)
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Reconnaissance airplane by Armstrong Whitworth.
Engine: 120/160 hp Beardmore
Armament: 1 Vickers/1 Lewis
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed: 83.5/95 mph @ 6500 ft
Ceiling: 12000 ft
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Bomber by Martinsyde.
Engine:
Armament:
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed:
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Fighter by Nieuport.
Engine: 1 Le Rhône rotary engine (Type 17) with 89 kW (119 HP) or 1 Clerget (Type 17bis) with 97 kW (130 hp)
Armament: 1 7.7 mm Vickers or Lewis machinegun
The Nieuport Type 17 was its manufacturer’s most important model and one of the most important fighter planes of the Allies in World War I. As the culmination of Nieuport’s development of fighter scouts, it was so successful that it was adopted by most of the Allies, including Russia and the United States. Many top pilots from World War I flew this aircraft, appreciating its manoeuvrability and high climbing capacity. (Source: Aircraft of the World, IMP BV)
Span: 8.2 m (27 ft)
Length: 5.96 m (19.5 ft)
Height: 2.44 m (8 ft)
Wing surface: 14.75 m² (158.76 ft²)
Empty weight: 374 kg (824.5 lbs)
Max. Weight: 560 kg (1234.5 lbs)
Max. speed: 170 km/u (
Ceiling: 5350 m (17.552 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A by Nieuport.
Engine:
Armament:
Span:
Length:
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed:
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Observation airplane by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine: Air-cooled 12 cylinder V-engine RAF 4a 112kW (150hp)
Armament: 2 or 3 7.7 mm MG's and maximum 116 kg bombs (2x51kg or 4x29kg or 8x9kg)
Span: 12.98 m (42.5 ft)
Length: 8.5 m (27.8 ft)
Height: 3.47 m (11.3 ft)
Wing surface: 35.07 m² (377.5 ft²)
Empty weight: 717 kg (1580 lbs)
Max. Weight: 1301 kg (2868 lbs)
Max. speed: 164 km/h (102 mph)
Ceiling: 4115 m (13.500 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Observation airplane by Royal Aircraft Factory.
Engine: 1 x Hispano-Suiza V-8 149 kW
Armament: 1 x 7.7 mm Vickers machine-gun + 1 x 7.7 Lewis machine-gun + 4 x 18.6 kg bombs
The S.E.5a was one of the best observation aircraft of the First World War. It was designed by H.P. Folland at the Royal Aircraft Factory in Farnborough. After overcoming a few teething problems, the best British pilots achieved great success with it. Despite its angular shape, the well-proportioned S.E.5a was extremely fast and formed a very stable weapon platform. These were all characteristics that compensated for its somewhat lacking manoeuvrability. (Source: Aircraft of the World, IMP BV)
Span: 8.12 m
Length: 6.38 m
Height: 2.9 m
Wing surface: 22.67 m²
Empty weight: 635 kg
Max. Weight: 887 kg
Max. speed: 218 km/u
Ceiling: 6705 m
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Fighter/Bomber by Sopwith Aviation Company.
Engine: 1 Clerget 99.7 kW (130hp)
Armament: 2 x 7.7 mm machineguns
believed to have been thus nicknamed for the fact that its cabane struts appeared to be interplane struts cut in half, the 1 1/2 Strutter was the first British aeroplane fitted with an interrupted gun, complemented by a trainable gun in the rear cockpit. First flown in December 1915 with an 82 kW (110 hp) Clerget rotary, the type resulted from a naval requirement and showed such capability that large-scale production was undertaken with the naval and army designations Admiralty Type 9700 and Two-seater respectively. The type was produced in two- and single-seat forms, the latter being a bomber operated almost exclusively by the navy. Deliveries began in spring 1916, and total British production of 1513 1 1/2 Strutters was complemented by about 4500 French-built aircraft. Replacement with more agile fighters of higher performance began in July 1917. (source: The International Encyclopedia of Aircraft, Oriole Publishing, 1991)
Span: 10.21 m (33.5 ft)
Length: 7.97 m (26.1 ft)
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight: 974 kg (2150 lbs)
Max. speed: 161 km/h (100 mph)
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Fighter by Sopwith Aviation Company.
Engine: 1 x Hispano-Suiza V-8 149 kW (200 hp)
Armament: 3 or 4 x 7.7 mm machine-guns + 4 x 11.3 kg bombs
Unlike earlier Sopwith fighters the Dolphin was powered by a static engine, and the deep fuselage virtually filled the gap between the backward-staggered wings so that the pilot sat with his head protruding through a gap in the upper-wing centre section for superb fields of vision in the upper hemisphere. The prototype flew in May 1917 with a 149 kW (200 hp) Hispano-Suiza geared engine, and the same powerplant was used in the Dolphin Mk I that began to enter service late in 1917. Problems with the geared engine then led to the Dolphin Mk III with a direct-drive version of the same engine, and the designation Dolphin Mk II was used for a few aircraft with a 224 kW (300 hp) Hispano-Suiza direct-drive engine. Production totaled 1532, but only 621 were issued to operational squadrons, which disliked the Dolphin’s unusual stalling characteristics and the vulnerability of the pilot in the nose-over landing accident. (Source: The International Encyclopedia of Aircraft, Oriole Publishing, 1991)
Span: 9.91 m (32 ft 6 in)
Length: 6.78 m (22 ft 3 in)
Height:
Wing surface:
Empty weight:
Max. Weight:
Max. speed: 180 km/h (112 mph)
Ceiling:
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate:
A Fighter by Sopwith Aviation Company.
Engine: 1 x Clerget 9-cylindre air-cooled piston engine 97 kW (131 hp)
Armament: 2 x 7.7 mm Vickers machine-guns + 4 x 11.35 kg bombs
In terms of aircraft destroyed (1294) the Camel was the best British fighter of World War I, and 5490 examples were built. The type was derived conceptually from the Pup, and began to enter service in mid-1917. The nickname Camel resulted from the forward-fuselage hump over the two machine-guns. Power was provided by any of four rotaries in the range from 75 to 112 kW (100 to 150 hp), and the concentration of the major masses (engine, fuel, armament and pilot) round the centre of gravity in the forward fuselage gave the fighter exceptional agility, though the turning characteristics were tricky enough to cause all but experienced pilots some acute handling problems. There was also a naval 2F.1 version with a single gun, reduced span and a detachable tail. (Source: The International Encyclopedia of Aircraft, Oriole Publishing, 1991)
Span: 8.53 m (28 ft)
Length: 5.72 m (18.7 ft)
Height: 2.6 m (8.5 ft)
Wing surface: 21.46 m² (231 ft²)
Empty weight: 421 kg (928 lbs)
Max. Weight: 659 kg (1453 lbs)
Max. speed: 188 km/h (117 mph)
Ceiling: 5790 m (18.996 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate: 3000 m (9842 ft) in 10'
A Fighter by Sopwith Aviation Company.
Engine: 1 Le Rhône rotary engine 60kW (80 hp)
Armament: 1 7.7 mm Vickers machinegun and max 11.3 kg Cooper-bombs
Span: 8.08 m (26.5 ft)
Length: 6.04 m (19.8 ft)
Height: 2.87 m (9.4 ft)
Wing surface: 23.6 m² (254 ft²)
Empty weight: 357 kg (787 lbs)
Max. Weight: 556 kg (1226 lbs)
Max. speed: 180 km/h (112 mph)
Ceiling: 5335 m (17.503 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate: to 4907 m (16.099 ft) in 35 minutes
A Fighter by Sopwith Aviation Company.
Engine: 1 aircooled 9-cylindre Clerget 9B rotary engine 96.9 kW (130 hp)
Armament: 1 7.7 mm Vickers machinegun
Span: 8.08 m (26.5 ft)
Length: 5.94 m (19.4 ft)
Height: 3.2 m (10.4 ft)
Wing surface: 21.46 m² (231 ft²)
Empty weight: 450 kg (992 lbs)
Max. Weight: 642 kg (1415 lbs)
Max. speed: 187 km/u (116 mph)
Ceiling: 6250 m (20.505 ft)
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate: to 3050 m (10.000 ft) in 10.5 minutes
A Fighter by Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés.
Engine: 1 V8 Hispano-Suiza 8Ab engine in line - 134 kW (180 hp)
Armament: 1 7.7 mm machinegun (500 rounds)
Span: 7.82 m (25.6 ft)
Length: 6.08 m (19.9 ft)
Height: 2.2 m (7.2 ft)
Wing surface: 17.85 m² (192 ft²)
Empty weight: 500 kg (1102 lbs)
Max. Weight: 705 kg (1554 lbs)
Max. speed: 212 km/u (131 mph)
Ceiling: 6550 m (
Endurance: 2.75 hours
Climb rate: 421 m/min (1381 ft/min)